用户流失预警项目实战[大数据培训]
更新时间:2019年11月08日11时57分 来源:传智播客 浏览次数:
1、项目简介
当下我们生活的环境中,经常会有各种购物平台、淘宝平台、京东平台等等,我们都是其中的用户之一,如果咱们长时间不用某一平台,可能会收到某某平台的促销信息,那么平台为什么给我们发这个消息呢,显然平台是经过数据分析,他会分析我们不用这个平台的可能性有多大(即对于平台来说流失用户的可能性有多大),现在拿到某平台的一组数据,进行建模分析。这里将尝试使用多种分类器来验证预测效果。
·数据收集
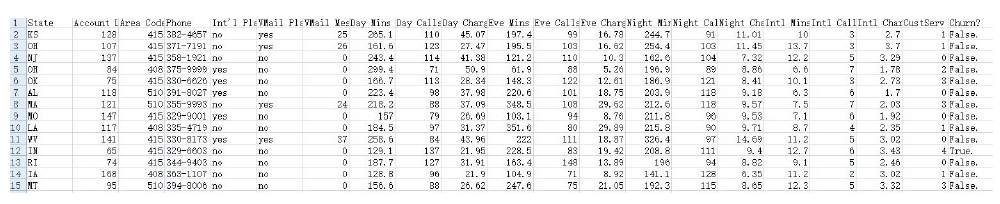
·环境需求
Anaconda3 + pycharm + numpy + pandas + scikitlearn + SVM+RF+KNN
·运行结果
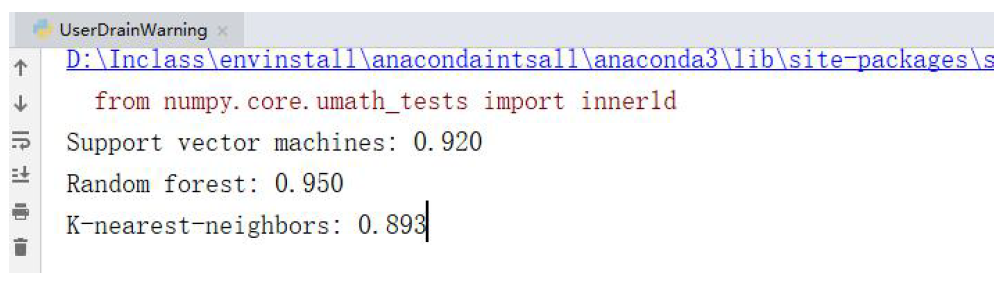
2. 代码实现
#TODO:用户流失预警 #1.导包 from __future__ import division import pandas as pd import numpy as np #2.加载数据与观察数据 churn_df = pd.read_csv('UserDrain_data/churn.csv') col_names = churn_df.columns.tolist() # print("Column names:\n",col_names) # print(churn_df.shape) #(3333, 21) # Column names:['State', 'Account Length', 'Area Code', 'Phone', "Int'l Plan", 'VMail Plan', 'VMail Message', 'Day Mins', 'Day Calls', 'Day Charge', 'Eve Mins', 'Eve Calls', 'Eve Charge', 'Night Mins', 'Night Calls', 'Night Charge', 'Intl Mins', 'Intl Calls', 'Intl Charge', 'CustServ Calls', 'Churn?'] to_show = col_names[:6] + col_names[-6:] #前6 列与后6 列 # print(len(to_show))#共12 列 # print ("\nSample data:\n",churn_df[to_show].head(6)) # State Account Length Area Code ... Intl Charge CustServ Calls Churn? # 0 KS 128 415 ... 2.70 1 False. # 1 OH 107 415 ... 3.70 1 False. #2.1 类别编码 churn_result = churn_df['Churn?'] y = np.where(churn_result == 'True.',1,0) #2.2 删除不需要对应列数据 to_drop = ['State','Area Code','Phone','Churn?'] churn_feat_space = churn_df.drop(to_drop,axis=1) #yes 或者no 需要转化为布尔类型数据 yes_no_cols = ["Int'l Plan","VMail Plan"] churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] = churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] == 'yes' # print(churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols]) # Int'l Plan VMail Plan # 0 False True # 1 False True # 获取数据属性名 features = churn_feat_space.columns # print("churn_feat_space:\n",churn_feat_space.head()) # Account Length Int'l Plan ... Intl Charge CustServ Calls # 0 128 False ... 2.7 1 # 1 107 False ... 3.7 1 #将dataframe 转化为ndarray 数组,同时数组中的元素类型为float 类型 #对应的布尔类型的值,True 为1,False 为0 X = churn_feat_space.as_matrix().astype(np.float) np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.NaN) # print("churn_feat_space.as_matrix().astype(np.float):\n",X) # [[128. 0. 1.... 3. 2.7 1.] # [107. 0. 1.... 3. 3.7 1.] # 2.3 数据标准化 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler scaler = StandardScaler() X = scaler.fit_transform(X) # print("Feature space holds %d observations and %d features" % X.shape) #3333 行17 列 # Feature space holds 3333 observations and 17 features # print("Unique target labels:", np.unique(y))# [0 1] # print(X[0]) #标准化之后的第一行数据 #[ 0.67648946 -0.32758048 1.6170861 1.23488274 1.56676695 0.47664315 # 1.56703625 -0.07060962 -0.05594035 -0.07042665 0.86674322 -0.46549436 # 0.86602851 -0.08500823 -0.60119509 -0.0856905 -0.42793202] # print(len(y[y == 0])) #2850 #3.KFold K 折交叉验证 from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold def run_cv(X,y,clf_class,**kwargs): #创建kfold 对象 kf=KFold(len(y),n_folds=5,shuffle=True) y_pred=y.copy() #迭代 count=0 for train_index,test_index in kf: count=count+1 #y 对应的标签数量:3333 # print("train_index 数量:",len(train_index)) #train_index 数量: 2666 # print("test_index 数量:", len(test_index)) # test_index 数量: 667 # print(test_index) X_train,X_test=X[train_index],X[test_index] y_train=y[train_index] #初始化一个分类器模型 clf=clf_class(**kwargs) clf.fit(X_train,y_train) y_pred[test_index] = clf.predict(X_test) # print("迭代次树:", count)#5 return y_pred #4.建模 from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier as RF from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as KNN def accuracy(y_true,y_pred): # NumPy interprets True and False as 1. and 0. return np.mean(y_true == y_pred) #4.1 SVM / RF /KNN 三种算法预测准确率 print("Support vector machines:","%.3f" % accuracy(y, run_cv(X,y,SVC))) print("Random forest:","%.3f" % accuracy(y, run_cv(X,y,RF))) print("K-nearest-neighbors:","%.3f" % accuracy(y,run_cv(X,y,KNN)))
推荐了解:传智播客大数据课程
















 AI智能应用开发
AI智能应用开发 AI大模型开发(Python)
AI大模型开发(Python) AI鸿蒙开发
AI鸿蒙开发 AI嵌入式+机器人开发
AI嵌入式+机器人开发 AI运维
AI运维 AI测试
AI测试 跨境电商运营
跨境电商运营 AI设计
AI设计 AI视频创作与直播运营
AI视频创作与直播运营 微短剧拍摄剪辑
微短剧拍摄剪辑 C/C++
C/C++ 狂野架构师
狂野架构师





















